Cardiovascular and Cardiometabolic Comorbidities Are Frequently Observed in Patients With Narcolepsy
Research has demonstrated an increased prevalence of certain comorbid conditions, including cardiovascular (CV) and cardiometabolic conditions, in patients with narcolepsy compared with matched controls.1,2
CV Comorbidities
An increased prevalence of cardiovascular and cardiometabolic conditions, such as hypertension, obesity, diabetes, and hypercholesterolemia has been reported in people with narcolepsy compared with matched controls1,2
- In one study, the odds of heart disease in patients with narcolepsy were twice those of control subjects. Hypertension and hypercholesterolemia were also more frequently observed in the narcolepsy group than in the control group.2
- Additionally, a separate study showed that the prevalence of obesity, diabetes, and stroke was significantly increased in patients with narcolepsy compared with controls.1
- The risk and presence of comorbid conditions may further complicate both diagnosis and disease management.1,13,14
The pathophysiology of narcolepsy, which involves hypocretin deficiency,15 may partially explain the increased incidences of cardiovascular comorbidities seen in patients with narcolepsy10-12
- Preclinical data suggest that sleep and proper release of hypocretin protect against the development of atherosclerosis10—a disease of the arteries characterized by the deposition of plaques of fatty material on their inner walls.16
- Clinical research also suggests that the nondipping nocturnal blood pressure (BP) profile frequently observed in patients with narcolepsy may be partly due to hypocretin deficiency and disrupted nighttime sleep.11,12
- In the general population, atherosclerosis and blunted nocturnal BP dipping are independent risk factors for CV disease, CV events, and mortality.16-21
Some risk factors for CV disease are modifiable3-12
CV Comorbidities
Increased Risk of Comorbid Conditions
in Patients With Narcolepsy*
in Patients With Narcolepsy*
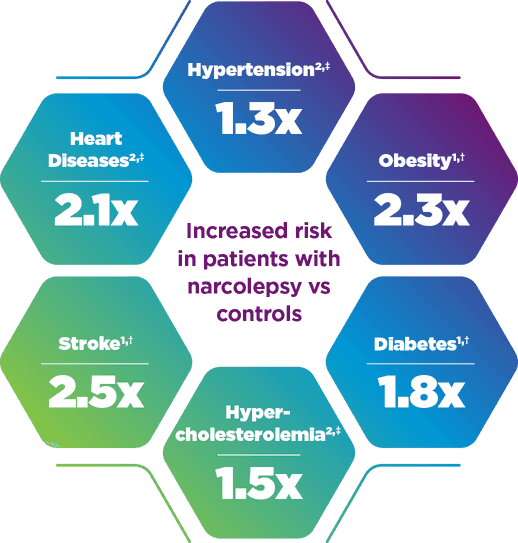
*Odds ratios in patients with narcolepsy vs controls without narcolepsy.
†Odds ratio is from a retrospective analysis of US medical claims data for 93,122 people with narcolepsy and a control group of 46,559 people without narcolepsy.1
‡Odds ratio is from an interview study of 320 patients with narcolepsy compared with a matched general population sample of 1464 participants.2
- Black J, Reaven NL, Funk SE, et al. Medical comorbidity in narcolepsy: findings from the Burden of Narcolepsy Disease (BOND) study. Sleep Med. 2017;33:13-18.
- Ohayon MM. Narcolepsy is complicated by high medical and psychiatric comorbidities: a comparison with the general population. Sleep Med. 2013;14(6):488-492.
- Whelton PK, Carey RM, Aronow WS, et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA guideline for the prevention, detection, evaluation, and management of high blood pressure in adults: executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines [published correction appears in Hypertension. 2018;71(6):e136-e139] [published correction appears in Hypertension. 2018;72(3):e33]. Hypertension. 2018;71(6):1269-1324.
- Jackson SL, King SM, Zhao L, Cogswell ME. Prevalence of excess sodium intake in the United States—NHANES, 2009-2012. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2016;64(52):1393-1397.
- Benjamin EJ, Muntner P, Alonso A, et al; American Heart Association Council on Epidemiology and Prevention Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2019 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2019;139(10):e56-e528.
- Lloyd-Jones DM, Hong Y, Labarthe D, et al. Defining and setting national goals for cardiovascular health promotion and disease reduction: the American Heart Association's strategic Impact Goal through 2020 and beyond. Circulation. 2010;121(4):586-613.
- Salehi-Abargouei A, Maghsoudi Z, Shirani F, Azadbakht L. Effects of Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH)-style diet on fatal or nonfatal cardiovascular diseases—incidence: a systematic review and meta-analysis on observational prospective studies. Nutrition. 2013;29(4):611–618.
- Quan SF. Sleep disturbances and their relationship to cardiovascular disease. Am J Lifestyle Med. 2009;3(1 suppl):55s-59s.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sleep and sleep disorders. Sleep and Chronic Disease. https://www.cdc.gov/sleep/about_sleep/chronic_disease.html. Page last reviewed: August 8, 2018.
- McAlpine CS, Kiss MG, Rattik S, et al. Sleep modulates haematopoiesis and protects against atherosclerosis. Nature. 2019;566(7744):383-387.
- Dauvilliers Y, Jaussent I, Krams B, et al. Non-dipping blood pressure profile in narcolepsy with cataplexy. PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e38977.
- Grimaldi D, Calandra-Buonaura G, Provini F, et al. Abnormal sleep-cardiovascular system interaction in narcolepsy with cataplexy: effects of hypocretin deficiency in humans. Sleep. 2012:35(4):519-528.
- Thorpy MJ, Hiller G. The medical and economic burden of narcolepsy: implications for managed care. Am Health Drug Benefits. 2017;10(5):233-241.
- Thorpy M, Morse AM. Reducing the clinical and socioeconomic burden of narcolepsy by earlier diagnosis and effective treatment. Sleep Med Clin. 2017;12(1):61-71.
- American Academy of Sleep Medicine. Central disorders of hypersomnolence. In: The International Classification of Sleep Disorders – Third Edition (ICSD-3) Online Version. Darien, IL: American Academy of Sleep Medicine; 2014.
- Herrington W, Lacey B, Sherliker P, Armitage J, Lewington S. Epidemiology of atherosclerosis and the potential to reduce the global burden of atherothrombotic disease. Circ Res. 2016;118(4):535-546.
- Frostegård J. Immunity, atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease. BMC Med. 2013;11:117.
- Hermida RC, Ayala DE, Mojón A, Fernández JR. Blunted sleep-time relative blood pressure decline increases cardiovascular risk independent of blood pressure level—the “normotensive non-dipper” paradox. Chronobiol Int. 2013;30(1-2):87-98.
- Ohkubo T, Hozawa A, Yamaguchi J, et al. Prognostic significance of the nocturnal decline in blood pressure in individuals with and without high 24-h blood pressure: the Ohasama study. J Hypertens. 2002;20(11):2183-2189.
- Ben-Dov IZ, Kark JD, Ben-Ishay D, Mekler J, Ben-Arie L, Bursztyn M. Predictors of all-cause mortality in clinical ambulatory monitoring: unique aspects of blood pressure during sleep. Hypertension. 2007;49(6):1235-1241.
- GBD 2013 Mortality and Causes of Death Collaborators. Global, regional, and national age–sex specific all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990–2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet. 2015;385(9963):117-171.